If you’re earning U.S.-sourced income, understanding the difference between Form W-8 and Form W-9 is critical. These IRS forms play a crucial role in determining your tax status, withholding rates, and compliance with U.S. tax laws.
Whether you’re a U.S. citizen, nonresident, or part of a foreign entity, the form you submit determines how your income is taxed—and whether you’re hit with unnecessary withholding or reporting issues. This guide will help you understand each form, when and why it’s needed, and how to stay compliant.
What is Form W-9?
Form W-9 is used by U.S. persons, such as citizens, resident aliens, and independent contractors, to provide their Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)—like an SSN or EIN—to the person or business that pays them. This information enables the payer to issue Form 1099 and accurately report income earned to the IRS.
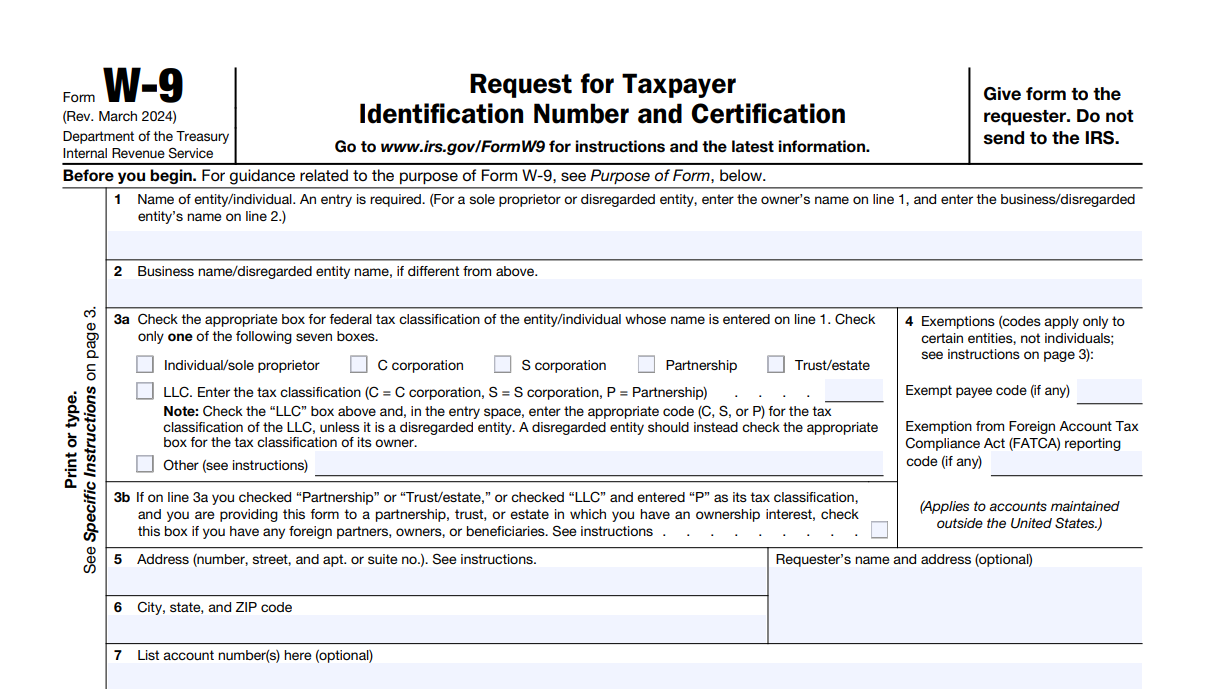
Key Uses:
- Required for U.S. citizens, resident aliens, or domestic entities.
- Used to report income from services, interest, dividends, or other income-related activities.
- Must be submitted to clients or employers—not to the IRS directly.
- Often required during onboarding for freelancers and contractors before receiving any payments.
- Essential for preparing Form 1099-NEC at year-end.
Important Notes:
- If not submitted, the contractor may be subject to backup withholding.
- Failure to file Form W-9 could mean no 1099, affecting your tax filing.
- W-9 forms do not expire unless your information changes (e.g., name, business name, or federal tax classification).
What is Form W-8?
Form W-8 is used by non-U.S. citizens, nonresidents, and foreign entities to certify their foreign status and to claim tax treaty benefits where applicable. These benefits may allow for reduced or no United States tax withholding on income received from U.S. sources.
Unlike W-9s, W-8 forms are not submitted to the IRS, but must be given to the withholding agent, such as the U.S. company or financial institution making the payment.
Types of W-8 Forms:
- W-8BEN – For foreign individuals making a foreign person’s claim for tax treaty benefits.
- W-8BEN-E – For foreign entities such as corporations or partnerships.
- W-8ECI – For income effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business.
- W-8EXP – For foreign governments, foreign tax-exempt organizations, and other foreign organizations.
- W-8IMY – For foreign intermediaries or foreign flow-through entities acting as intermediaries between a U.S. withholding agent and foreign persons, ensuring the correct amount of tax is withheld for compliance with U.S. tax regulations.
Key Uses:
- Proves foreign status and tax residency outside the U.S.
- Enables reduced withholding rates via tax treaty claims.
- Required before a foreign person can receive income from U.S. sources.
- Confirms the beneficial owner is not a U.S. person.
Important Notes:
- W-8BEN and W-8BEN-E are valid for 3 years, unless your status or information changes.
- If the correct W-8 form is not provided, the payer must withhold 30% on eligible payments.
- Forms must include a foreign TIN and permanent residence address.
W-8 vs. W-9: Key Differences at a Glance
[table “35” not found /]When to Use Each Form
Use Form W-9 if you:
- Are a U.S. citizen, resident alien, or domestic business.
- Are being paid as a contractor, freelancer, or vendor.
- Need to submit your TIN so your income can be reported correctly via Form 1099.
Use Form W-8 if you:
- Are a non-U.S. citizen, nonresident, or a foreign entity.
- Will receive income from U.S. sources like royalties, interest, or services.
- Want to claim treaty benefits to reduce or avoid U.S. tax withholding.
- Need to confirm you’re the beneficial owner of the income, not a pass-through.
Expert Help for Getting It Right
Choosing between W-8 vs. W-9 isn’t just about paperwork—it’s about filing the correct form to ensure accurate tax reporting, avoid excessive tax withholding, and stay compliant with IRS regulations. Whether you’re a U.S. citizen submitting a W-9 with your social security number or a nonresident using Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E to claim tax treaty benefits, providing the right taxpayer identification number protects you from unnecessary penalties.
At 1040 Abroad, we specialize in U.S. expat taxes. If you’re unsure about your tax status, eligibility for tax treaty reductions, or how to navigate tax forms like W-8 and W-9, we offer free tax advice to all U.S. expats. Reach out anytime—our experts are here to help you pay taxes accurately, legally, and confidently.







